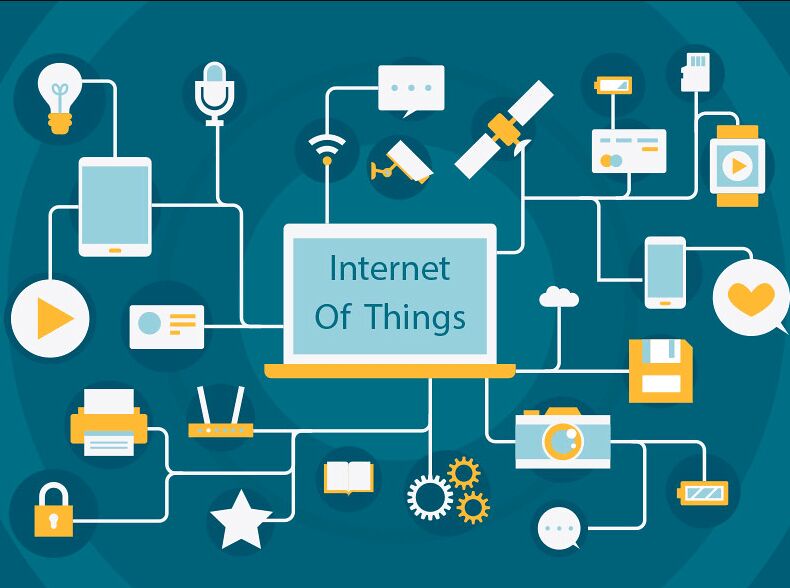
To understand how IoT (internet of things) affects our lives in our smart homes, the cities we live in, and our lives. We need to grasp our knowledge of what IoT is. The internet of things explains the cluster of physical objects comprising sensors, software, and other technological devices to interlink and exchange data with other devices and systems. The internet of things also refers to the skyrocketing number of digital devices. These devices share data by communicating through the internet all over the world. You can control these devices remotely through a user interface or even your smartphones. In fact next-generation technologies like IoT, AI are transforming our homes and living.
Technology Advancing
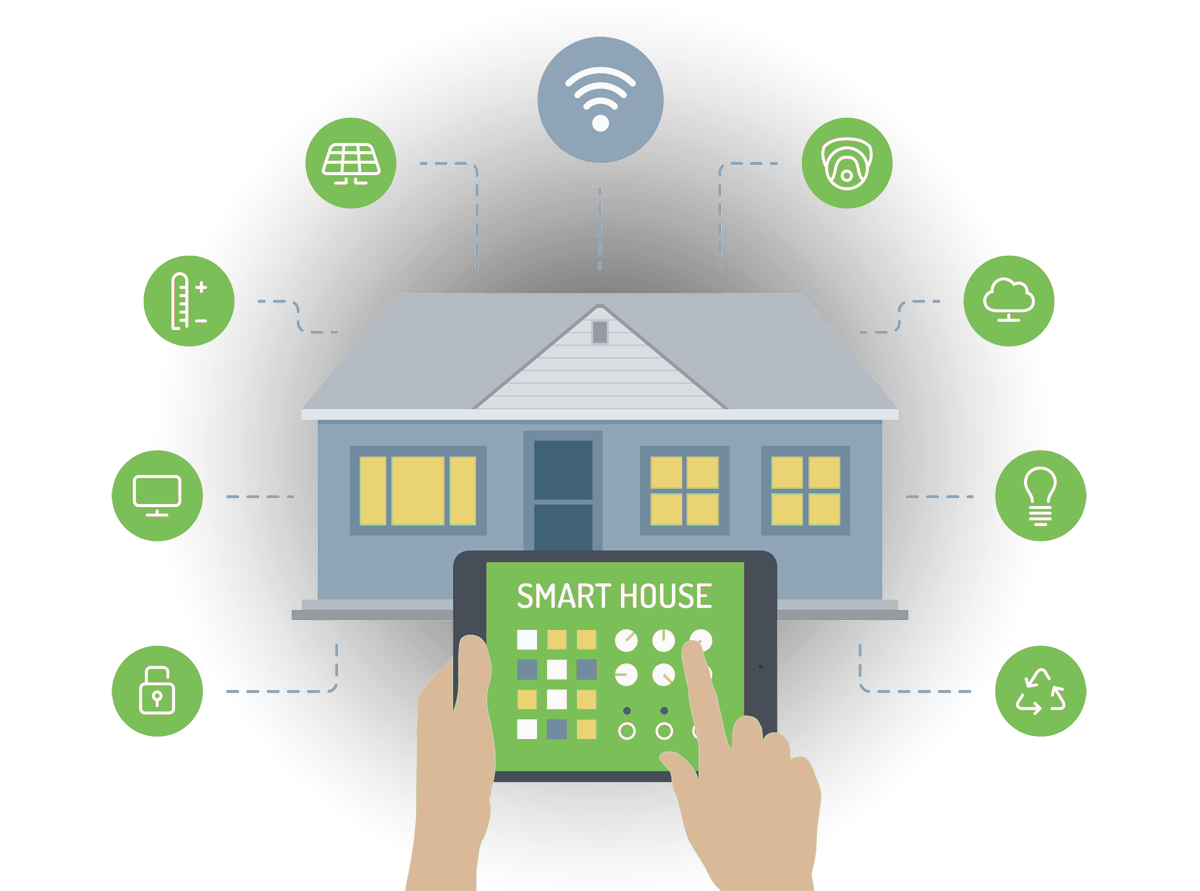
Because of technological advancements in our digital society, embedded systems, user-interactive software, control systems, wireless sensor systems, and more enable the internet of things. The consumer market relates IoT technology to the concept of smart homes, which includes devices such as home security systems, thermostats, lighting, and cameras. All these devices include Bluetooth. They can use the internet to share data and store data in a database to support an ecosystem.
Because it enables the data to be shared, users can control devices via devices linked to the ecosystem, such as smartphones.
To What Extent Does It Affect Our Lives?
IoT has changed the way we carry out simple tasks, and it has made our lives convenient since we can control devices around us by the touch of a screen on our smartphones. Before IoT, people would physically get up to do things around the house, such as turn on the water heater or turn the lights on.
IoT also includes mobile devices; since they can communicate with others and manage data, it is a device everywhere. Everyone carries a smartphone all day. You can control objects using a mobile device.
Today, you can get brilliant smart refrigerators with work-in cameras, so you can look at their substance while you are shopping. In the future, you will see fridges that detect you are coming up short on supplies and send an essential food rundown to your cell phone.
Stores could then push suggestions to add food and different things, considering previous purchases and average purchasing patterns. When strolling through the supermarket, reminders will get sent to your smartphone to ensure you never need to make that second trip back to the store.
Using IoT can decimate costs for firms that are operating in the economy. Organizations use IoT for innovative management and for observing scattered data. Thus, they can handle the latter from far-off places as they feed data into applications and information stockpiling (data storage).
IoT gives the benefit of realizing things ahead of time. Because of the minimal expense of IoT, it is now possible to screen and manage previously inaccessible activities. The monetary aspect is the best benefit since this innovation could replace people responsible for observing and keeping up with provisions. Therefore, expenses can essentially decrease and get optimized. IoT likewise makes it conceivable to gain new bits of knowledge. For example, they are associating the climate impact with mechanical production.
Concerns About IoT
One of the critical drivers of the IoT is information. The accomplishment of interfacing gadgets to make them more productive is subject to access to capacity and data preparation. For this reason, organizations dealing with the IoT gather information from many sources and store it in their cloud network for additional handling.
The data is vulnerable, and hackers target it to access private information. This welcomes protection and security risks and single point weakness of different frameworks.
Conclusion on IoT and its Impact
The future of IoT is limitless. It gives solutions in all areas, including production, style, medical services, schooling, etc. Innovative sites can share a typical smart city platform, which bonds well, particularly for tiny urban communities. The cloud-based nature of IoT solutions for Smart Cities gets fitted by sharing a stage dependent on the information. Small urban communities can shape a typical metropolitan ecosystem.
Along these lines, small and enormous smart cities’ solutions get organized and controlled through the central cloud platform. At last, yet critically, the size of a town isn’t a snag while heading to becoming “smart.” Urban communities in each group can profit from insightful technological advancements.