What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is the pay-as-you-go service for IT resources over the internet. Rather than building, owning, and maintaining their own IT infrastructure, businesses can use cloud providers like IBM, Microsoft Azure, and AWS to access technology resources such as computing capacity, storage, and databases on a pay-as-you-go basis. Cloud computing brought possibilities that were not available for small to medium-level corporations before.
There are three types of Cloud Computing
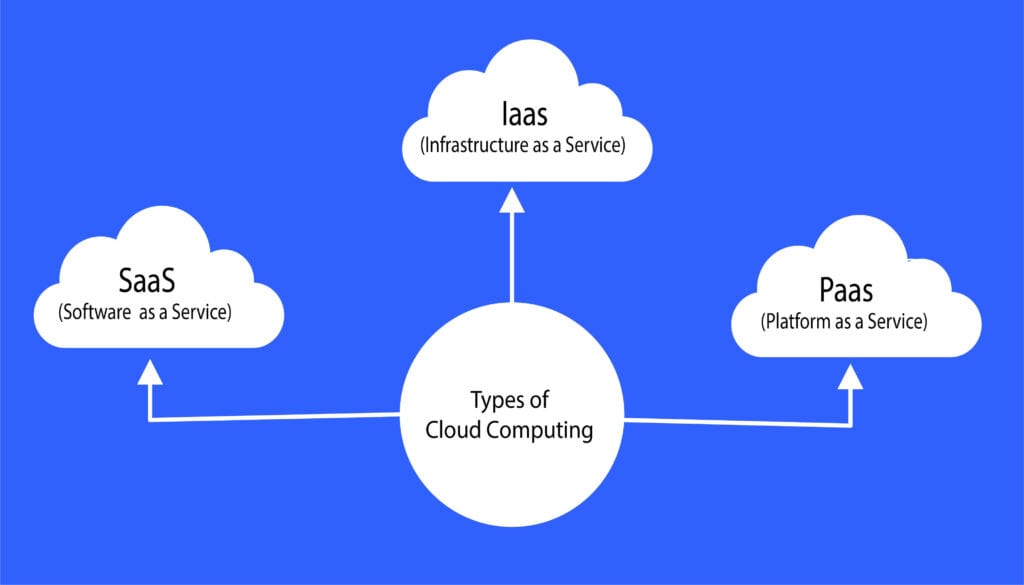
IaaS (Infrastructure as a service)
IaaS Provides fundamental resources over the internet on the pay as you go, model. Resources like computing power, data storage, and virtual servers. The biggest advantage of IaaS is you can scale up your resources on demand and can scale down after peak hours. With IaaS your system will never have a shortage of resources when the demand arises.
PaaS (Platform as a Service)
PaaS provides resources to application developers on-demand like hardware, software development stack, and development tools. In PaaS, software developers don’t have to manage hardware or operating systems and this gives them the freedom to focus on just development and deployment.
SaaS (Software as a Service)
SaaS is a cloud-based application that is hosted and managed by a service provider in the cloud. SaaS is the most famous type of cloud computing which impacts agriculture immensely. Promising startups are developing applications that farmers can use on their cell phones or computers to manage all farming processes.
Cloud computing applications in Agriculture
Cloud computing and agriculture are a beautiful marriage between the world’s oldest craft and the latest invention.
“As population increases and farmland remains limited, efficiency on the field and in the data center is imperative,” says Darren Patterson, vice president of technology at XS, Inc. “When you factor in a drought, it’s even more important to make the most of your resources.”
The following are some examples of particular applications:
Crop Management
Cloud Computing will be used to collect data on all crops grown in the recent past, allowing farmers to make informed decisions on what to plant next. Weather data: The cloud can also store weather data for specific regions as well as weather forecasts for specific time periods. Analysis of these Cloud Computing data will assist farmers in making crop-related decisions.
Soil Information
Soil information is also essential for crop decision-making. Apart from the soil profile, it can also include a historical pattern of soil, which can be used to forecast future trends. Is the soil becoming more acidic/alkaline, or are there other changes in the quality and composition of the soil? Soil Information can be stored using Cloud Computing for easier storage and analysis.
Growth Tracking
In different regions and at regular intervals, the growth of various crops can be controlled. This allows for the comparison of current growth trends to previous growth patterns. Cloud Analytics can be applied to the stored data to provide growth tracking insights
Farmers’ Information
Cloud Computing can be used by Authorities can store data of local farmers like the type of crops, yields, lands, and type of help they need. Data is important for better resource allocation and future strategies.
Expert Consultation
Cloud Computing facilitates solutions to common problems that farmers encounter is available. Experts also offer solutions to particular issues, with a relatively quick response time. There are several cloud computing platforms available where they provide solutions to farmers like Telemedicine. Farmers contact these platforms through their app or website and get a solution to their problem right away.
E-Commerce
People in rural areas are unable to easily sell their own products directly to the market. Between the retail and production ends, a slew of middlemen springs up, resulting in farmer exploitation. Farmers may sell their produce directly to end users/retailers using cloud computing’s agricultural management information system.
A web-based Agriculture management information system can be beneficial in the agriculture sector because it provides farmers in rural areas with the most up-to-date information on weather, markets, fertilizer, crop sowing, and other topics.
Practical Information Sharing
Agriculture research station scientists will share their own discoveries and recommendations about modern cultivation techniques and fertilizer use in the cloud.
Conclusion
Start-up companies are creating market applications that are directly beneficial to the agricultural sector. Farmers may use any of these apps to build budgets and operating schedules based on their production plans. Agriculture-specific software is available, allowing for more effective workforce management. Work schedules can also be made based on weather forecasts, and progress can be tracked. Machine operations and production can be measured using mobile task management systems and data integration techniques.